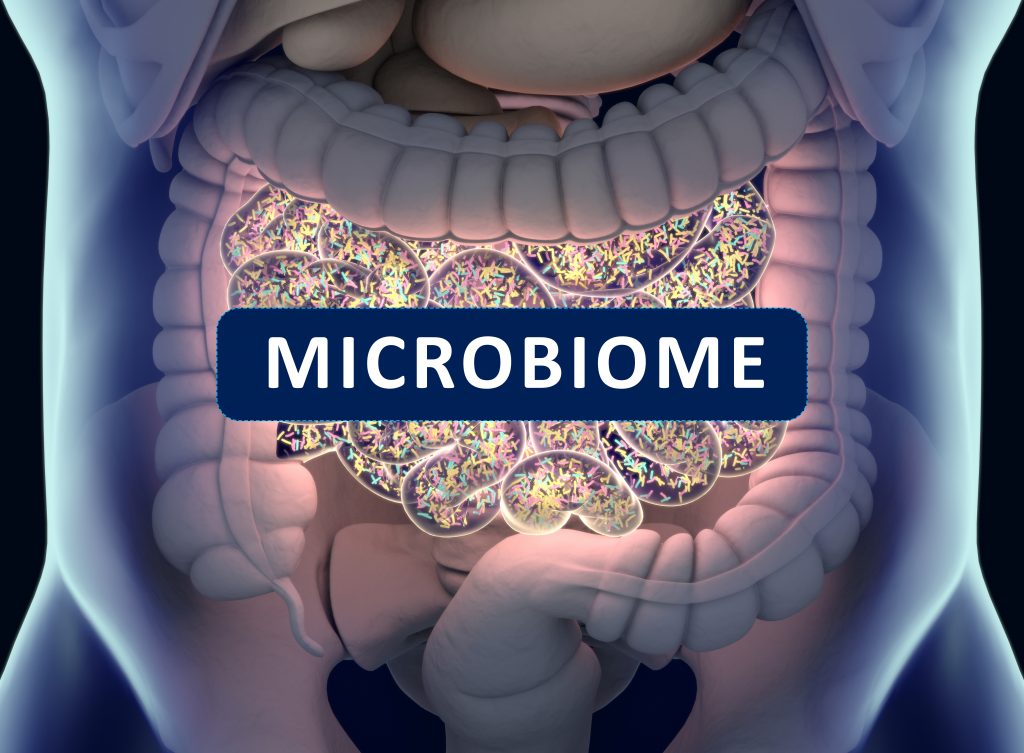
Gut health is important because it actually impacts your whole body. Your gut is where you digest your food and get the nutrients you need, but it’s a stew in there; and some ingredients can harm you. No pun intended. Did you know that your body can be a host for trillions of viruses, fungi, and bacteria? These microscopic organisms mostly live in the large intestine and are commonly known as the gut microbiome. When you have a healthy balance of bacteria in your gut, and it’s called equilibrium. What’s happening in your gut can determine your mood, your sleep habits, even your complexion. So, how healthy is your gut?
So what is gut health
For a good grasp of gut health, you need to understand how the gut microbiome works. The microorganisms in your body are scientifically referred to as microbes. They mostly live in the large intestine in what’s known as the cecum. Bacteria are believed to be the most beneficial of all the microbes in the body.
Did you know that an average human body contains about 10 trillion more bacterial cells than human cells? Science has revealed about a thousand different bacteria species in a human’s body, and each is believed to play a unique role. And even though there may be some harmful bacteria species in your body, most are considered essential for your health. For your gut biome to be considered healthy, it has to contain more healthy microbes than harmful ones. If the bad bacteria outweigh the good ones, then your health may be compromised in surprising ways.
The gut microbiome’s effect on the body
From the moment you’re born, right up to your last breath, your microbiome affects your health. The microbiome is believed to control digestion and many other body processes, including the immune system and the central nervous system. Some scientists have concluded that without the microbiome, you would not be able to survive.
How do you know that your gut is healthy? You can check your gut health yourself. Companies like My Psomagen have sites you can check out for information about how you could test your microbiome.
How gut health affects the body
Your gut relies on just the right balance of different bacteria to digest your food and to prevent infection and inflammation. Gut health also affects your mental health, weight, blood sugar, and liver. Prebiotic foods (whole grains, bananas, greens, onions, garlic, soybeans, and artichokes) act as food for healthy gut bacteria. Probiotic foods like yogurt are full of good bacteria already. Your gut microbiome is believed to help with some essential body processes, such as the following:
Why fiber impacts gut health
As we said, there are numerous bacteria species in the human gut. And of those, some feed on fiber. That’s why you need a lot of it. This bacteria helps with the digestion of carbohydrates that produce short-chain fatty acids, which are good for your gut health and prevent conditions such as obesity, heart disease, and diabetes. Fiber is also believed to be a great nutrient for weight loss and the reduction of cancer.
How probiotic foods boost your microbiome
Probiotic foods contain beneficial live microbiota that may further alter one’s microbiome. These include fermented foods like kefir, yogurt with live active cultures, pickled vegetables, tempeh, kombucha tea, kimchi, miso, and sauerkraut. These foods can help prevent bad bacteria from multiplying. If bad bacteria increase, they could cause diseases like irritable bowel syndrome and inflammatory bowel disease.
Can gut healthy foods affect your mood as well as your body
Yes, your diet affects your mood. A Mediterranean diet, rich in whole grains, legumes and seafood as well as nutrient-dense leafy vegetables that are high in the fiber, promotes a diverse population of helpful bacteria in the gut. Research suggests that a healthy gut microbiome may be important in the processing of neurotransmitters like serotonin that regulate mood.
“Our imaging studies show that the brains of people who follow a Mediterranean-style diet typically look younger, have larger volumes and are more metabolically active than people who eat a more typical Western diet,” said Dr. Lisa Mosconi, the director of the Women’s Brain Initiative at the Weill Cornell Medical Center in New York. Such brain benefits may be protective against the onset of dementia, she said.
Some research has suggested that the gut microbiome produces chemicals that may help develop your brain function. This could also help with your cognitive functions and memory loss.
Now that you know how important gut health is, keep an eye on your own and get the balance you need.
More Health Articles To Read
How Does Methadone Treatment Aid Recovery